It’s easy to get lost when navigating the world of credit card processing. Credit card processing is a complex system with a panoply world of credit card processing of terms that are important to understand. Why? Because different payment processing solutions can be a portion of a lot of profit and, equally, a big expense for small- and medium-sized business owners.
Here is a glossary featuring the most common payment processing terms you will come across as a business owner:

Glossary of terms
-A-
Acquiring bank/acquirer: A bank or financial institution that processes credit card transactions for business owners (see merchant). It issues interchange fees and is a licensed member of Visa or MasterCard. Acquiring banks maintains merchant accounts.
-C-
Card association/card network: Card-issuing organizations that license and manage payment cards. The most well-known ones are Visa and Mastercard. However, there are others. The logos are either on the front or back of your card.
Cardholder: The owner of a debit or credit card- your customers! Cardholders may purchase goods or services online or in person.
Card-not-present transaction (CNP): A transaction where the credit card isn’t present. You take CNP payments when your customers purchase something from you, either online or over the phone.
Card-present transaction (CPT): A transaction where the card is present, such as when your customer makes a purchase in-store. Their card is read by a card reader that is connected to your POS system, tablet or smartphone, or contactless terminal.
Chargeback: This happens when your customer or issuing bank disputes a transaction, and it is sent back through the interchange to your acquiring bank (or merchant account) to be resolved.
Credit card: A payment card issued by a bank to purchase goods or services on credit.
Credit card payment services: A service that allows businesses to accept payments from customers using credit cards. These services typically provide businesses with a credit card terminal or a virtual terminal that will enable them to process card payments in person or online.
-D-
Debit card: A card your customer uses to access funds from their checking account. These funds are withdrawn immediately, either to purchase goods or services or can be transferred to another account.
Digital payment services: Digital payment services are electronic payment systems that allow businesses to make and receive payments using digital means, rather than cash or checks. Some examples of digital payment services include PayPal, Google Pay, and Apple Pay.
-E-
EMV: This stands for Europay, MasterCard, Visa, but it now includes American Express, Discover, UnionPay, and JCB. EMV cards have smart chips embedded to prevent fraud at point-of-sale (POS). These cards usually require PINs or signatures.
-I-
Interchange fees: Fees are charged for every debit or credit card transaction that you make. They are paid by your acquiring bank (also called acquirer or merchant bank) to your issuing bank (or card issuer). Interchange fees are determined by card associations and vary depending on the type of card used.
Issuing bank/card issuer: A bank or financial institution that issues credit cards on behalf of your card association, such as Visa, or Mastercard. Respective card associations license them to do so and bear financial responsibility for all transactions made by the cardholder. In other words, they are the intermediary between your card association and the cardholder-your customer.
-M-
Merchant: This refers to you. An individual or business owner that processes card payments through a merchant account (or an acquiring bank).
Merchant account: This is opened by a business owner like you through a merchant bank (also called an acquiring bank or acquirer) to accept debit, credit card, or ACH transactions.
Merchant processing: Merchant processing refers to the process of accepting and processing payment transactions made with credit and debit cards.
Merchant processing rates: Merchant processing rates are fees that merchants pay to accept and process payment transactions made with credit and debit cards. These fees are usually a percentage of the transaction amount and sometimes include a fixed fee per transaction.
-P-
Point-of-sale (POS): The location where customers pay for their goods and services, colloquially known as the cash or cash register. Point-of-sale can also refer to the hardware or software that you use to process transactions.
POS terminal: An electronic handheld device used to process your business's debit and credit card transactions.
Payment gateway: This is an essential technology for business owners to process online debit and credit card transactions. With a payment gateway, your customer’s payment information is securely sent, using encryption, to your acquiring bank for payment acceptance.
Payment cards: Credit or debit cards are used by your customers to make purchases.
Payment card industry (PCI) compliance: The payment card industry (PCI) sets security standards that your business must adhere to keep your consumers' personal information safe from fraud, hacking, or system vulnerabilities.
Payment processor: A third-party company that processes your business's debit or credit card transactions. Payment processors usually offer various merchant solutions such as payment gateways, security features, customer support, and others.
Payment process: Here is how the payment terms featured in this glossary fit into the payment process.
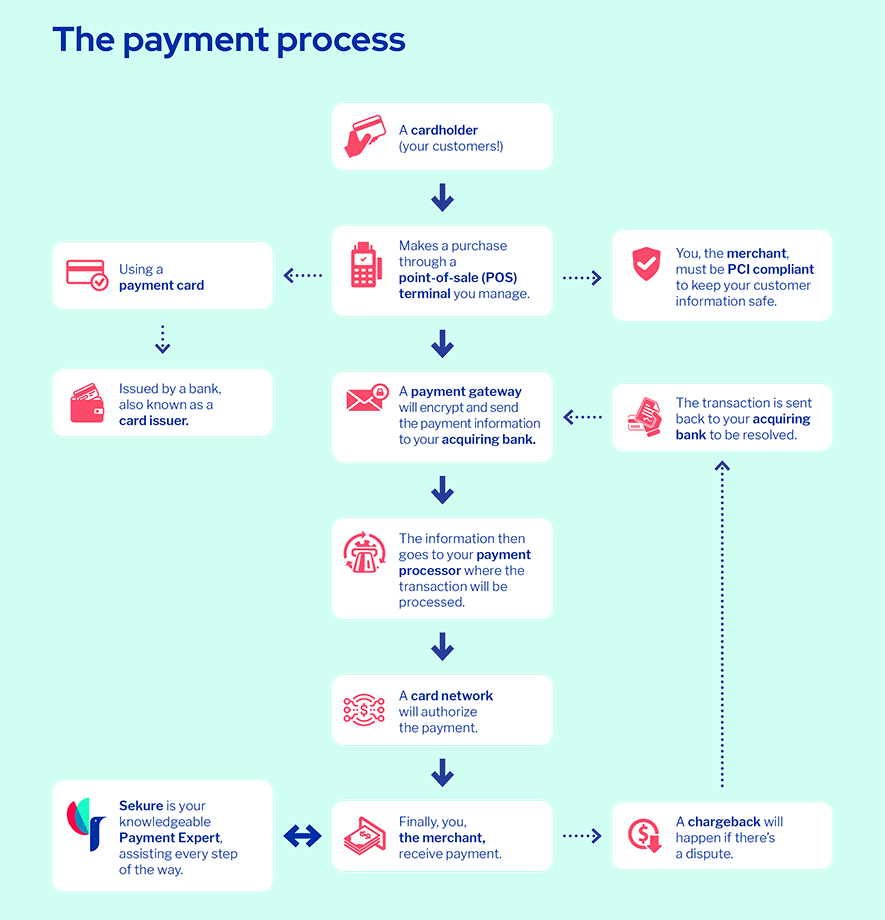
-O-
Online payment processing: The process of accepting payment transactions made through an online platform, such as a website or mobile app. Businesses can accept payments from customers using a variety of payment methods, including credit and debit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets.
Conclusion
You don’t need to spend more time pouring over your statements, trying to decipher the myriad of fees, charges, and transactions incurred. Instead, our Payment Experts can do a complete analysis of your statement and review it with you. Doing so will help you better understand your setup, which will undoubtedly lead you to identify how to save on fees.
Contact Sekure Payment Experts for additional assistance, such as upgraded equipment and top-of-the-line customer support, to help your business succeed.
Categories

